
On April 25, 2023, during the 8th anniversary seminar of the Energy Internet Research Institute and Forum of High-quality Development of Energy Think Tanks, Gao Feng, Deputy Director of the Energy Internet Research Institute, and Director of the Digital Transformation Research Lab of Tsinghua University, released the latest edition of a series of reports by the national high-end think tank of Tsinghua University - Progress in Energy Internet Research 2011-2020.

Introduction of the Progress in Energy Internet Research 2011-2020
Gao Feng
Apr 25 2023
“Internet +” smart energy (hereinafter referred to as Energy Internet) is the product of the integration and development of a new generation of information technology and energy technology. This has an important supporting role in achieving the strategic goals of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality, and solving global energy and environmental problems. As an enabler of the energy revolution Energy Internet will promote the development of a series of new technologies and new business models while helping solve global climate problems, to enable the clean, efficient, safe, convenient and sustainable use of energy. At present, various countries have made a lot of investments to build the innovation and research capabilities of the Energy Internet.
As such, the number of publications in the field of Energy Internet is growing rapidly worldwide. From the perspectives of development strategy, core technology, application and mechanism, the Department of Electrical Engineering, and the Energy Internet Research Institute of Tsinghua University have successively released a series of publications, such as Energy Internet Development Research, Energy Internet, The Development of National Energy Internet: Blue Book, The Development of National Energy Internet: Annual Report, etc. Compared to the aforementioned publications, Progress in Energy Internet Research 2011-2020 focuses on scientific research input and output, and adopts international comparative analysis, historical development analysis and other methodologies to provide industry authorities and researchers with a macro picture of the Energy Internet research on a longer time scale and a broader spatial scale. By releasing this report, we want to create a replicable, deepened and scalable research model. To this end, in the process of compilation, the team gave clear explanations and records on the research methods and data sources. The readers are encouraged to reproduce the analysis in the report.

Background of compilation of this report
Under the guidance of Professor Zeng Rong, Professor Sun Hongbin, and Professor Kang Chongqing, a compilation team of dozens of people, with Gao Feng as the Editor-in-Chief, was established. During the compilation, we received strong support from Shanxi Energy Internet Research Institute, as well as data support from Elsevier and Beijing Yingmaiqi Technology Co., Ltd.

The Compilation Team
The compilation team Consultants: Zeng Rong, Sun Hongbin, and Kang Chongqing Editor-in-Chief: Gao Feng Co-Editor-in-Chief: Guo Qinglai and Zhang Ning Associate Editor-in-Chief: Xia Yue and Jing Rui Editor: Cao Can, Wang Yanhe, Jin Yufen, Xu Lijuan, Song Yi, Qin Jianhua, and Lu Danni |
Supported by Energy Internet Research Institute of Tsinghua University Shanxi Energy Internet Research Institute Elsevier Beijing Yingmaiqi Technology Co., Ltd. |
Progress in Energy Internet Research 2011-2020 comprises 6 chapters. Chapter 1 introduces the basic research methods of the report after outlining the concept, characteristics and architecture of the Energy Internet. Chapter 2 shows the driving forces of the development of the Energy Internet, with the analysis of research projects, funding and researchers. Chapter 3 explores the hot topics of the Energy Internet, including word cloud diagrams, high-output research topics, and high-growth research topics. Chapter 4 presents the Energy Internet research results and their influences, showcasing various academic and patent works, institutional achievements, and research results from major countries, as well as their impacts. Chapter 5 introduces the research cooperation of Energy Internet, including cross-regional cooperation in academia, industry-university cooperation, and author cooperation network, as well as the present status of the international and domestic cooperation for patents, focusing on the R&D mode of Industry-University-Research cooperation, as well as the R&D mode of upstream and downstream cooperation. Chapter 6 outlines the trend of Energy Internet research, from academia to application and industrial promotion, by introducing similar typical Energy Internet demonstration projects involving multi-energy complementary systems, trading flexibility, and green and low-carbon at home and abroad.

The Overall Framework of the Report
Chapter 1 Overview 1.1 Introduction of Energy Internet 1.2 Methodology |
Chapter 5 Research Cooperation of Energy Internet 5.1 Academic Cooperation of Energy Internet 5.2 Patent Cooperation of Energy Internet 5.3 Comparison of Academic Cooperation and Patent Cooperation |
Chapter 2 Driving Force of the Development of Energy Internet 2.1 Projects and Funds of Energy Internet 2.2 Researchers of Energy Internet |
Chapter 6 Demonstration Projects of Energy Internet 6.1 Green and Low-Carbon Demonstration Projects 6.2 Smart Infrastructure Demonstration Projects 6.3 Multi-Energy Complementarity Demonstration Projects 6.4 Trading Flexibility Demonstration Projects 6.5 Energy Big Data Demonstration Projects |
Chapter 3 Hot Topics of Research of Energy Internet 3.1 Word Clouds of Energy Internet 3.2 High Output Topics of Energy Internet 3.3 High Growth Topics of Energy Internet 3.4 Comparison of Academic Topics and Patent Topics |
Appendix A Indicators Appendix B Data Sources Appendix C Topics Classification Appendix D Acronyms References |
Chapter 4 Energy Internet Research Results and Their Influences 4.1 Energy Internet research output and their influences 4.2 Research Results and Influence of Energy Internet Research Institutions 4.3 Research Results and Influence of Major Countries’ Activities 4.4 Comparison of the Academic research results and Patent filings |
|
Note: This page shows the overall framework of the report. The full table of contents can be found in the figure at the end of the article.
For this report, we searched various data pools by setting suitable keywords, and summarized and analyzed the retrieved results. First, according to the widely recognized core concepts of Energy Internet, the keywords for Energy Internet (EI), such as Energy Internet, smart grid, digital energy, microgrid, distribution network, integrated energy system, etc., were determined. Second, as Energy Internet means the interconnection of the energy and power system with the use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT), in order to reflect the multidisciplinary nature of Energy Internet and the completeness of the data analysis, ICT keywords (shown in the table below) were used to search the data in the field of energy and electricity. The literature retrieval involves the ICT keywords search in the “title/index keywords” fields in the sector of “energy and/or electricity”, and the ICT keywords search in relevant journals, as shown in the appendix of the report. The patent retrieval is a combination of ICT keywords and patent CPC codes to search for the patents with ICT keywords included in the “Title/Abstract/Claims” fields. According to the identified keywords and retrieval rules, the search and screening were carried out, and multiple sets of search results on different keywords were obtained. Then, the results were summarized and deduplicated. The final overall search results yielded a total of more than 100,000 academic publications, more than 190,000 patents, and more than 6,000 S&T research project funds. The data comes from patent databases of 126 countries or regions provided by Scopus, SciVal, Funding Institutional and Patsnap, and the legal information database of 120 countries or regions that provides the legal status of patents.
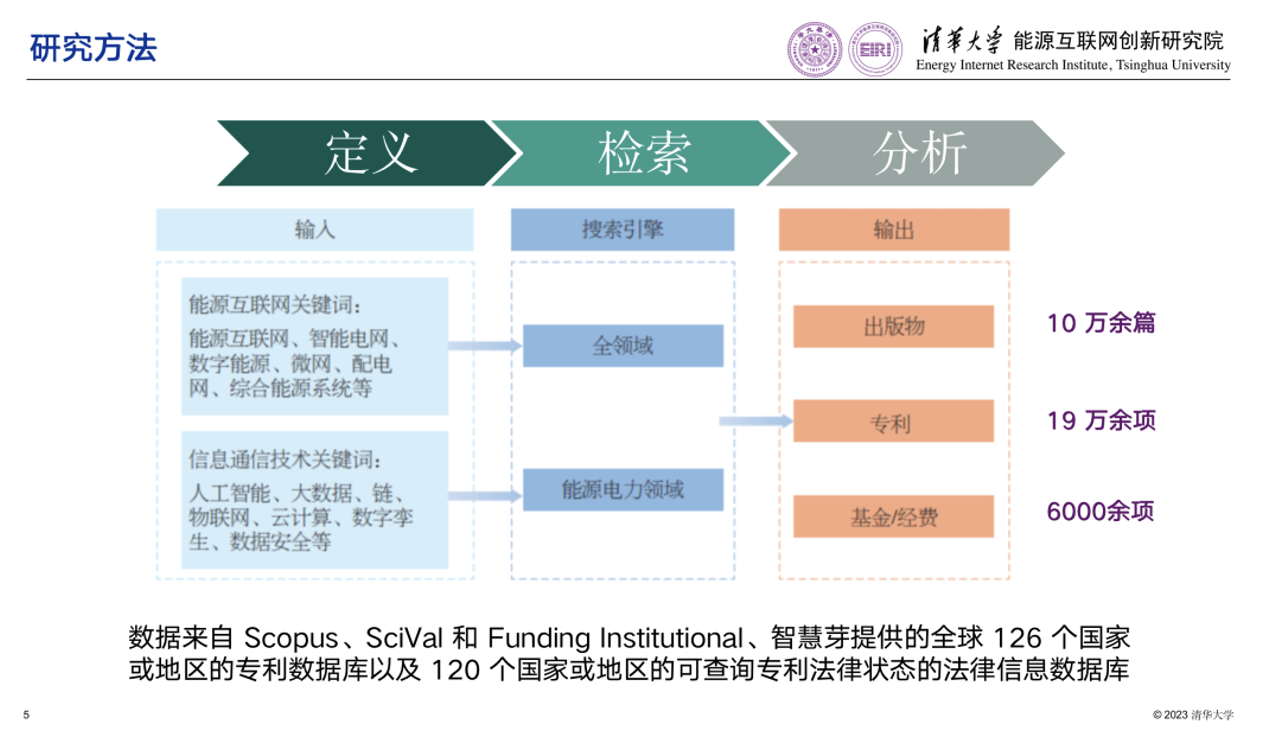
Methodology
Definition |
Retrieval |
Analysis |
|
Input |
Search Engine |
Output |
|
Energy Internet Keywords: Energy Internet, smart grid, digital energy, microgrid, distribution network, integrated energy system, etc. |
All domains |
Publications Patents Funds/Fares |
More than 100,000 publications
More than 190,000 patents
More than 6,000 funds |
ICT Keywords: AI, Big Data, chain, IoT, Cloud Compute, Digital Twin, Data Security, etc. |
Energy and electricity |
The data comes from patent databases of 126 countries or regions provided by Scopus, SciVal, Funding Institutional and Patsnap, and the legal information database of 120 countries or regions that provides the legal status of patents. |
The following examples illustrate how analysis is conducted.
Example 1: Number of Academic Researchers and Patent Filing Institutions
In the field of Energy Internet, changes in the number of researchers and patent filing institutions can reflect the interest in this field. Over the past 10 years, the attractiveness and influence of the Energy Internet sector have continuously increased with rapid growth both in the number of academic researchers and patent filing institutions. The number of academic researchers increased by more than 5 times, reaching 50,003, and the number of patent-filing institutions increased by nearly 4 times.
Before 2013, the United States led the way, in terms of the number of patent filing institutions in the field of Energy Internet. Since 2013, China has been the number one, and continues to expand its leading edge. It is particularly noteworthy that the overall growth rate of academic researchers and patent filing institutions in China from 2016 to 2020 was higher, when compared to that from 2011 to 2015. This was due to the guidance of the state on the development of “Internet +” smart energy since 2015. Thus, more research institutions have invested in the research of the field of Energy Internet.
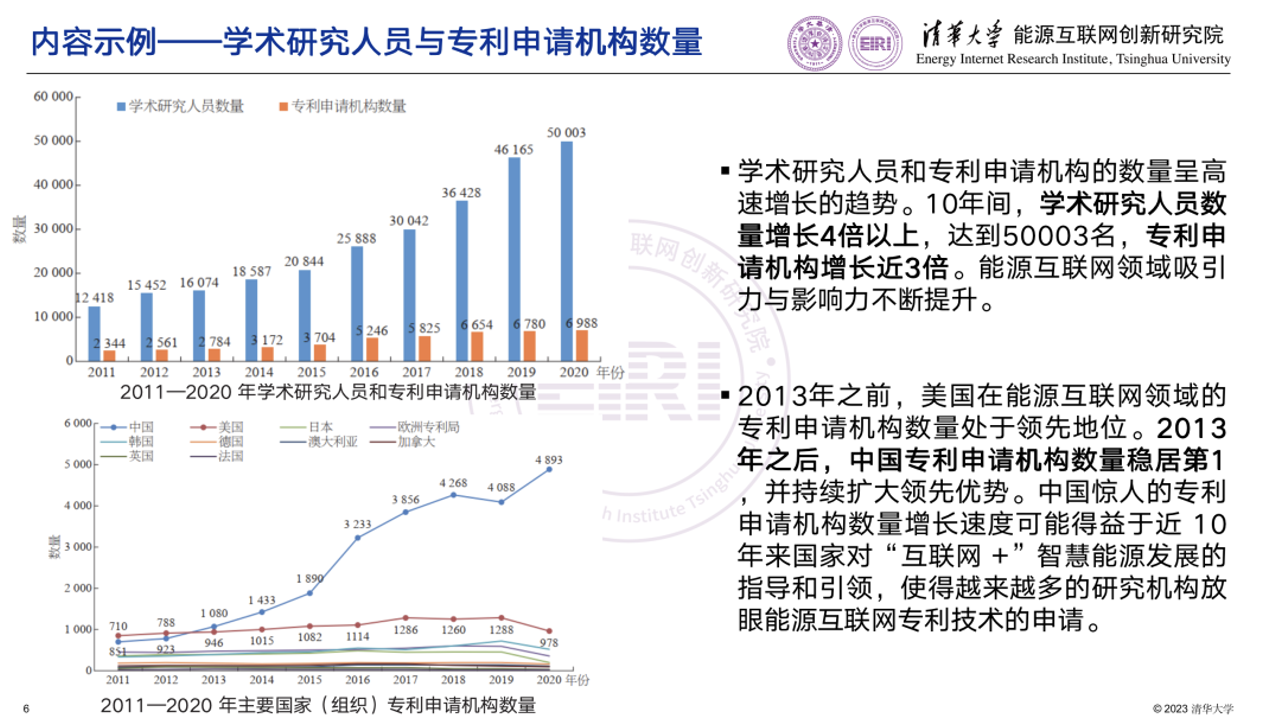
Example: Number of Academic Researchers and Patent Filing Institutions
Number of academic researchers and patent filing institutions in 2011-2020 |
The number of academic researchers and patent filing institutions exhibited rapid growth. In the past 10 years, the number of academic researchers increased by more than 5 times, reaching 50,003, and the number of patent filing institutions increased by nearly 4 times. The attractiveness and influence of the Energy Internet field is continuously improving. |
Number of patent filing institutions of major countries (organizations) in 2011-2020 |
Before 2013, the United States led the way, in terms of the number of patent filing institutions in the field of Energy Internet. After 2013, the number of Chinese patent filing institutions ranked first, and continued to expand its leading edge. This was due to the guidance of the state on the development of “Internet +” smart energy, promoting more research institutions to pay attention to patent filings related to Energy Internet. |
Example 2: Word Cloud of the Research Field of Energy Internet
This section explores the hot topics in the field of academic research and patent filings of Energy Internet and draws word clouds to analyze the development and changes of Energy Internet in two periods: from 2011 to 2017, and from 2018 to 2020. From 2011 to 2020, the academic research and patent filings of Energy Internet focused on the same direction, both showing great interest in the field of power systems, such as “Smart Grid” and “Microgrid”, which have always been hot topics in academic research, and “Power System”, which is a hot area in patent filings.
Compared to the period of 2011-2017, new keywords (red part of the Word Cloud of academic research) appeared in the academic research field of Energy Internet in 2018-2020, such as “Integrated Energy System”, “Machine Learning”, “Internet of Things”, “Alternating Current”, “Data-driven” and “Battery”, indicating that the interest of researchers in this field is gradually increasing. To a certain extent, this also signals the future development of the Energy Internet. In addition, from 2018 to 2020, academic research and patent filings for Energy Internet have shown the same interest in “Energy Storage”, “Distribution Systems” and “Energy Management Systems”.
From 2011 to 2020, the growing appearance of Energy Internet keywords (such as cyber-physical system, Internet of Things, integrated energy system, data-driven, blockchain, etc.) in the academic research field revealed that the attention and popularity of Energy Internet technologies continue to increase. The top 20 keywords in the field of Energy Internet patent filings were closely correlated to “electricity” “new energy” and “energy storage”, showing that Energy Internet is dominated by clean energy, and centred on electricity.
In addition to the time-scale-based keyword analysis shown in the examples, the report also provides a comparative analysis of hot academic research topics and patent filing topics in major countries and organizations, showing both the consistency and diversity of research interests in the field of Energy Internet among countries.
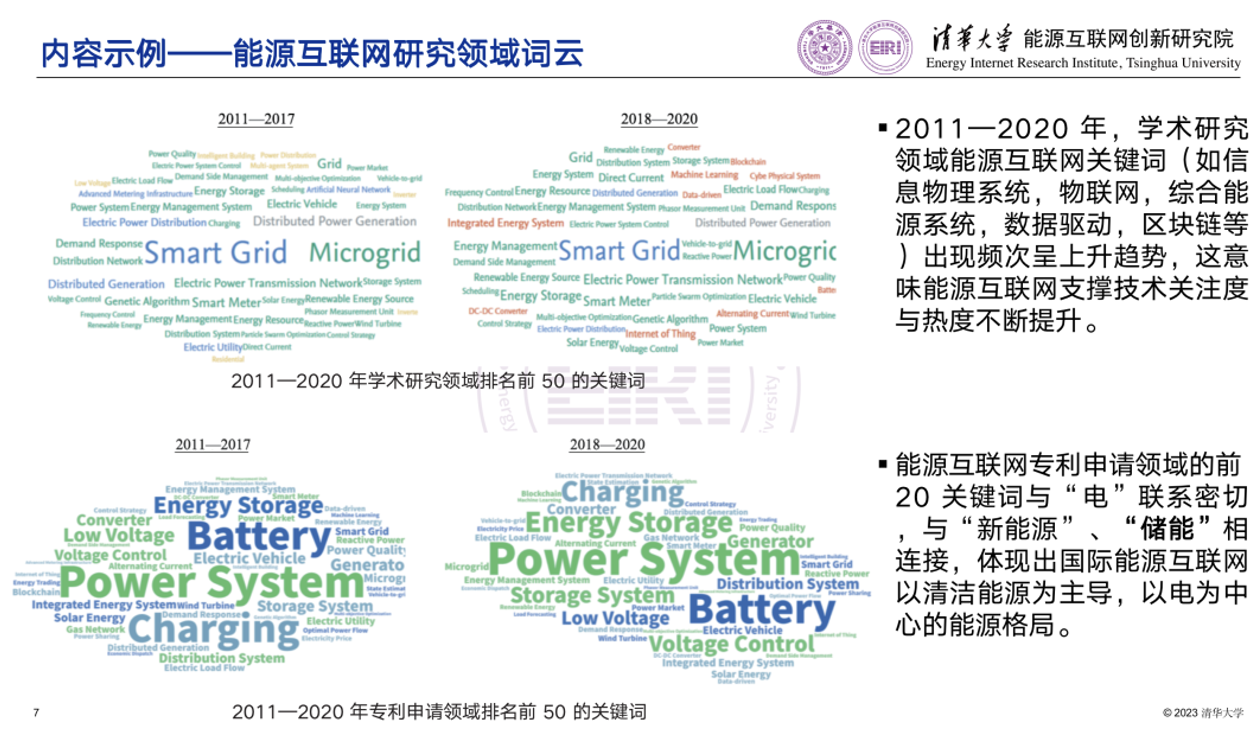
Example: Word Cloud of the Research Field of Energy Internet
Top 50 keywords in the academic field |
From 2011 to 2020, the growing appearances of Energy Internet keywords (such as cyber-physical system, Internet of Things, integrated energy system, data-driven, blockchain, etc.) in the academic research field revealed that the attention and popularity of Energy Internet technologies continue to increase. |
Top 50 keywords in patent filing |
The top 20 keywords in the field of Energy Internet patent filings are closely correlated to “electricity” “new energy” and “energy storage”, showing that the global Energy Internet is dominated by clean energy, and centered on electricity. |
Example 3: Research Results and Influence of Energy Internet Research Institutions
This example provides a comprehensive analysis of institutional publications in the field of Energy Internet. Among the world’s top 20 institutions in the field of Energy Internet, 15 institutions are from China, showing that China has great influence in this field. European and American countries, which are represented by the United States and Denmark, have a relatively high influence in terms of their research results, and China remains in the lead in terms of the number of publications. In general, institutions with a large number of publications in the field of Energy Internet do not necessarily have a high normalized impact factor value in their publications. Tsinghua University maintains a high level in terms of the number of research results and its influence.
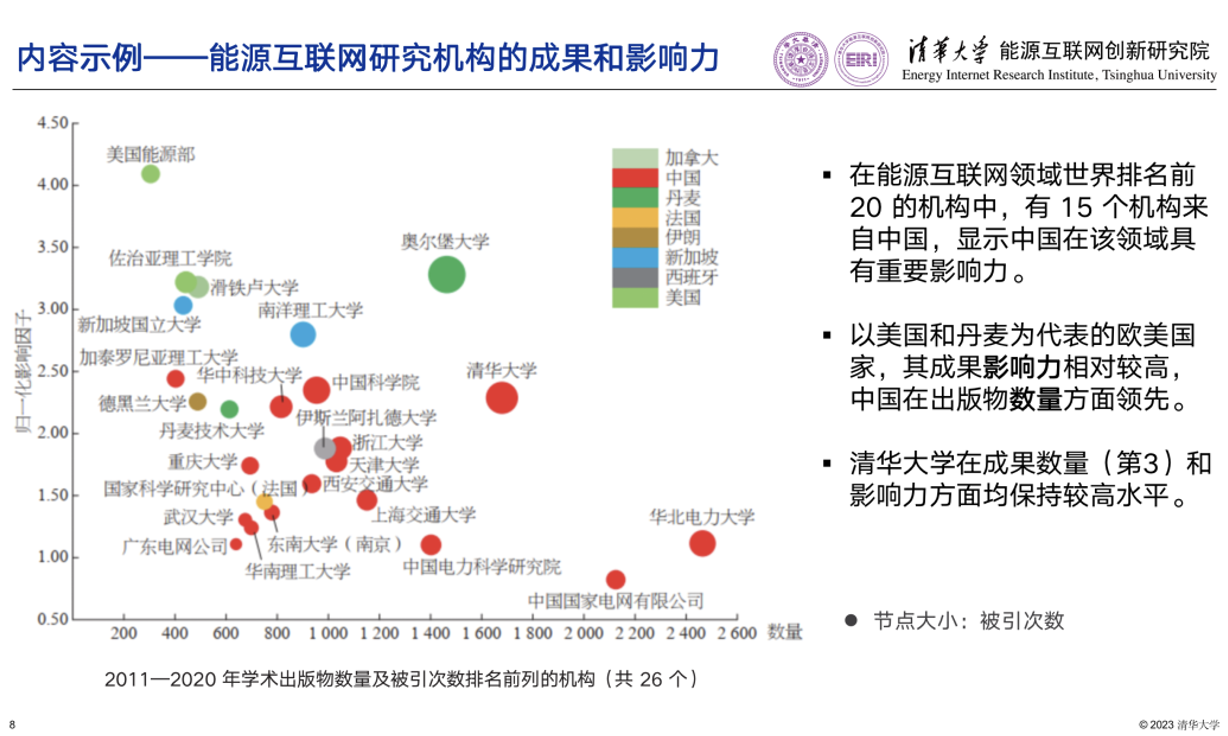
Example: Achievements and Influence of Energy Internet Research Institutions
|
Among the world’s top 20 institutions in the field of Energy Internet, 15 institutions are from China, showing that China has great influence in this field. |
|
European and American countries, which are represented by the United States and Denmark, have a relatively high influence in terms of their research results, and China remains in the lead in terms of the number of publications. |
|
Tsinghua University (ranked 3rd) maintains a high level, in terms of the number of research results and its influence. |
Leading institutions in terms of the number of publications and cites (26 in total). |
Size of nodes: number of cites |
Example 4: Energy Internet International Academic Cooperation
From the color of the nodes, it can be observed that the normalized impact factor value of Chinese publications (CHN) remains low, showing that there is still a large gap when compared to many other countries. From the thickness of the line, the number of cooperation publications of various countries (or regions) can be observed. The number of cooperated publications by China and the United States is the largest, and their quality is relatively higher. China's partnership network is very extensive, with major partners like the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, Singapore, and other countries.
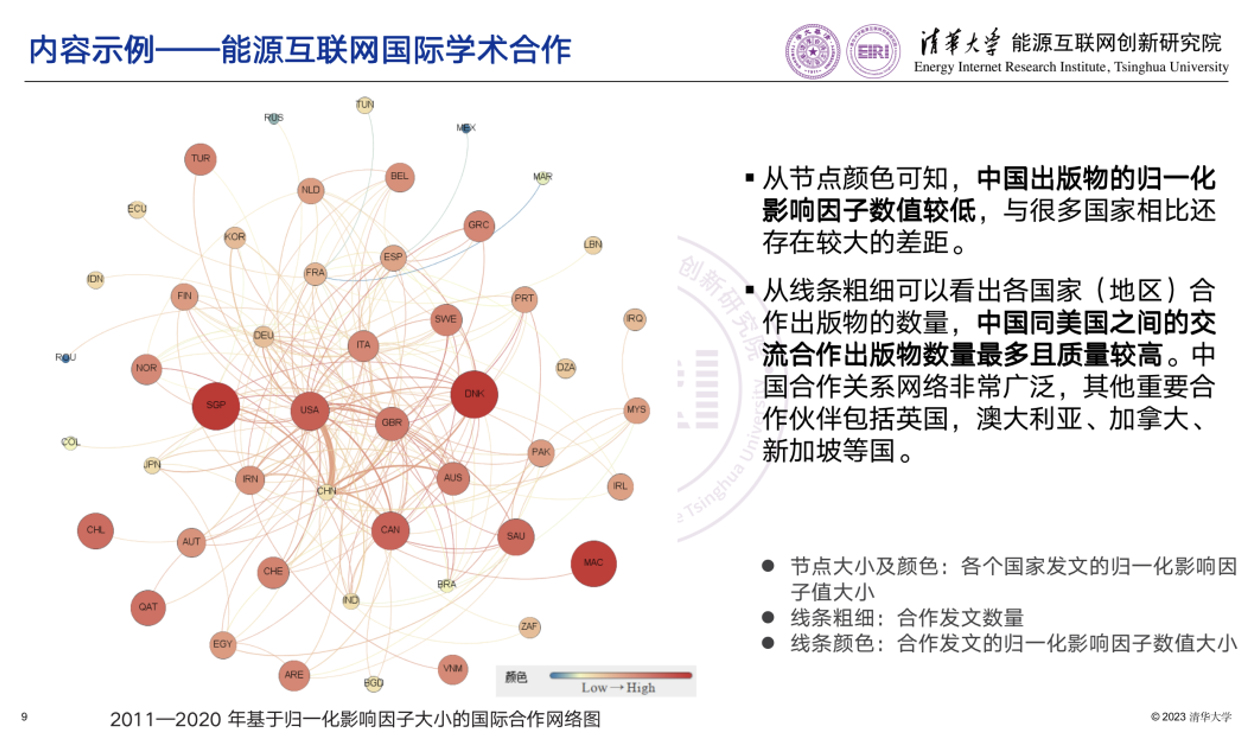
Example: Energy Internet International Academic Cooperation
|
From the color of the nodes, it can be observed that the normalized impact factor value of Chinese mainland publications (CHN) remains low, showing that there is still a large gap when compared to various countries. |
|
From the thickness of the line, the number of cooperation publications of various countries (or regions) can be observed, and the number of cooperated publications by China and the United States are the largest and, their quality is relatively higher. China’s partnership network is very extensive, with major partners like the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, Singapore, and other countries. |
|
Size and color of the nodes: normalized impact factor value of countries (or regions) |
|
Thickness of the lines: number of cooperated publications |
Global cooperation network map based on the normalized impact factor value from 2011 to 2020. |
Color of the lines: normalized impact factor value of cooperated publications |
To order the full report, please click the following link or scan the QR code. Due to limited time and capacity, there might be errors and omissions in the report, but most of the data and analysis can be improved. Please share with us your valuable comments and suggestions, and we hope that we can work together to push forward the scientific and technological innovation of the Energy Internet.
Contact person: Cao Can, ccan@tsinghua.edu.cn
Order link: (Tsinghua University Press official flagship store)
https://h5.m.taobao.com/awp/core/detail.htm?id=714226673089&fromPCToolkit=true

Thank you
Scan to order, or search the book title in Taobao
Please follow our WeChat public account: Energy Internet Research Institute of Tsinghua University
Please share your comments and suggestions
Contact person: Cao Can




